Minerals
Advanced Mineral Solutions for Modern Industries
At Sikander Corporation, we provide minerals all over Japan, catering to diverse industrial needs. Our high-quality mineral solutions are sourced, processed, and delivered with precision. From manufacturing to specialized industrial processes, we empower businesses with reliable and sustainable mineral resources that drive innovation and efficiency.
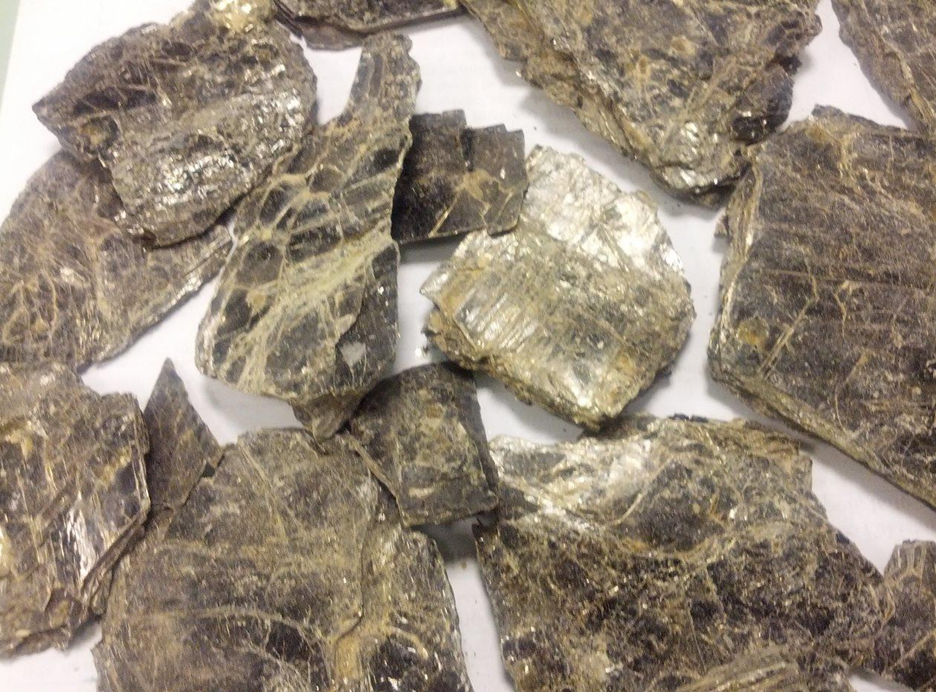
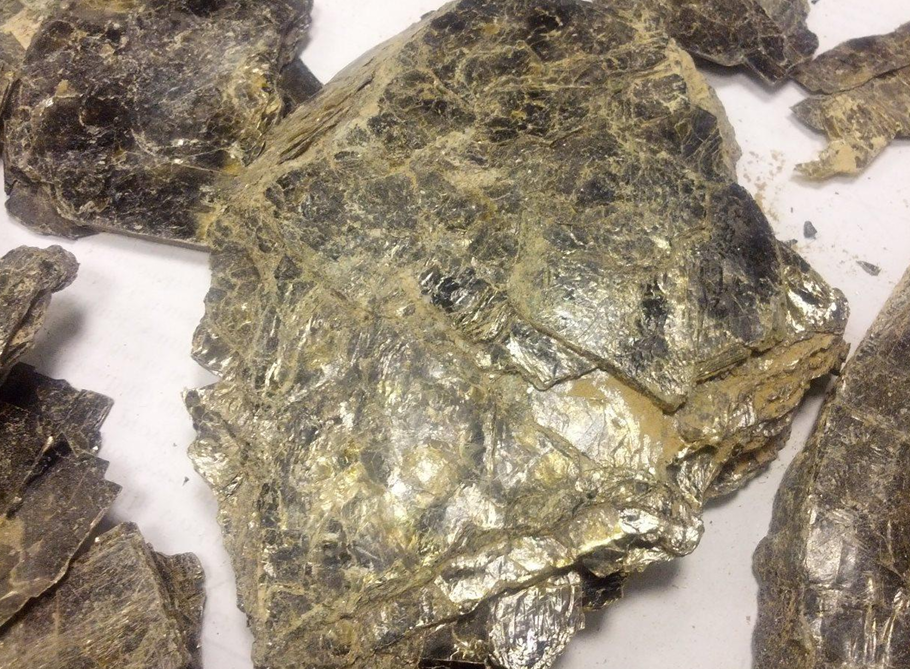
White Mica
White Mica, also known as Muscovite, is a naturally occurring silicate mineral recognized for its pearly luster, high heat resistance, and exceptional insulating properties. It appears in thin, transparent to opaque sheets with a silver-white to light-cream coloration. Due to its ability to split into fragile, flexible layers, white mica has been used for centuries in both traditional applications and modern industrial environments. Highly stable under extreme temperatures and chemically inert, white mica is widely valued in industries where durability, insulation, and purity are essential. It is also known for its smooth surface, excellent dielectric strength, and moisture resistance, making it one of the most versatile minerals for commercial use.
MUCOVITE (Uses)
JOINT COMPOUND
> The primary use of ground mica is in joint compound used to finish seams and blemishes in gypsum wallboard. The mica serves as a filler, improves the workability of the compound and reduces cracking in the finished product. In 2011 about 69% of the dry-ground mica consumed in the United States was used in joint compound.
PAINT
> Ground mica is used as a pigment extender in paint. It helps keep pigment in suspension; reduces chalking, shrinking and shearing of finished surface; reduces water penetration and weathering and brightens the tone of colored pigments. In some automotive paints tiny flakes of mica are used to produce a pearlescent luster.
DRILLING MUD
> Ground mica is an additive to drilling mud that helps to seal porous sections of the drill hole to reduce circulation loss. In 2011, about 17% of the dry-ground mica consumed in the United States was used in drilling muds.
PLASTICS
> The auto industry in the United States uses ground mica to improve the performance of plastic parts. In plastics, particles of ground mica serve as an agent to absorb sound and vibration. It can also improve mechanical properties by increasing stability, stiffness and strength.
RUBBER
> Ground mica is used as an inert filler and mold release agent in the manufacture of molded rubber products such as tires and roofing. The platy grains if mica act as an antisticking agent.
ASPHALT ROOFING
> Dry-ground mica is used as a surface coating on asphalt shingles and rolled roofing. The flat mica particles coat the surface and act as an antistick agent. The mica does not absorb the asphalt and stands up well to weathering.
COSMETICS
> Some of the highest quality ground mica is used in the cosmetics industry. The pearly luster of ground mica makes it an important ingredient in blushes, eyeliner, eye shadow, foundation, hair and body glitter, lipstick, lip gloss, mascara, and nail polish.
Sheet Mica Uses (White):
> Most sheet mica is used to make electronic devices. In these applications, the sheets are cut, punched, stamped, and machined to precise dimensions. Applications include diaphragms for oxygen breathing equipment, marker dials for navigation compasses, optical filters, pyrometers, retardation plates in helium-neon lasers, components for missile systems, medical electronics, optical instrumentation, radar systems, radiation detector windows, and calibrated capacitors. The quality of sheet mica is influenced by the presence of inclusions. These can impair splitting, decrease transparency, and reduce dielectric strength. Tiny crystals of staurolite, zircon, garnet, tourmaline, magnetite, hematite, and other minerals can form between the sheets and orient parallel to the mica's crystal structure. Inclusions decrease the mica's value and its suitability for use in most applications. Some of these involve creating mica sheets from ground mica composites or synthesizing micas in laboratories. Acrylic, fiberglass, nylon, polyester, styrene, vinyl-PVC, and vulcanized fibers are all being used as substitutes for sheet mica.



Specification & Quantity
Black Mica (Biotite)
Biotite has a small number of commercial uses. Ground mica is used as a filler and extender in paints, as an additive to drilling muds, as an inert filler and mold-release agent in rubber products, and as a non-stick surface coating on asphalt shingles and rolled roofing. It is also used in the potassium-argon and argon-argon dating methods for igneous rocks.
Uses of Black Mica (Biotite):
> Black Mica, commonly known as Biotite, is a dark, sheet-silicate mineral valued for its thermal stability, chemical resistance, and insulating properties. Due to its structure and durability, Biotite is used across multiple industrial sectors:
Industrial Uses:
- Electrical Insulation: Biotite's layered structure offers excellent dielectric strength, making it a valuable material for electrical insulation and heat-resistant components.
- Heat-Resistant Applications: Used in furnace linings, refractory products, and thermal barriers due to its ability to withstand high temperatures without degrading.
- Construction Materials: Ground biotite is mixed into cement, concrete, and asphalt to improve bonding, strength, and weather resistance.
- Ceramic Manufacturing: Added to ceramics and tiles to enhance durability, coloration, and thermal performance.
Geological & Scientific Uses:
- Petrological Studies: Biotite is a key mineral used in geological research to determine the age, composition, and metamorphic history of rocks.
- Soil Enrichment: Weathered biotite releases potassium and iron, contributing to the formation of nutrient-rich soils used in agriculture and land restoration.
Decorative & Commercial Uses:
- Countertops and Decorative Stones: Its shiny, dark flakes add aesthetic appeal to granites and decorative stones used in architecture and interior design.
- Crushed Mineral for Landscaping: Used as a decorative aggregate in gardens, pathways, and outdoor installations.
Metallurgical Uses:
- Fluxing Agent: Helps remove impurities during metal processing and improves the fluidity of molten materials.



Specification & Quantity
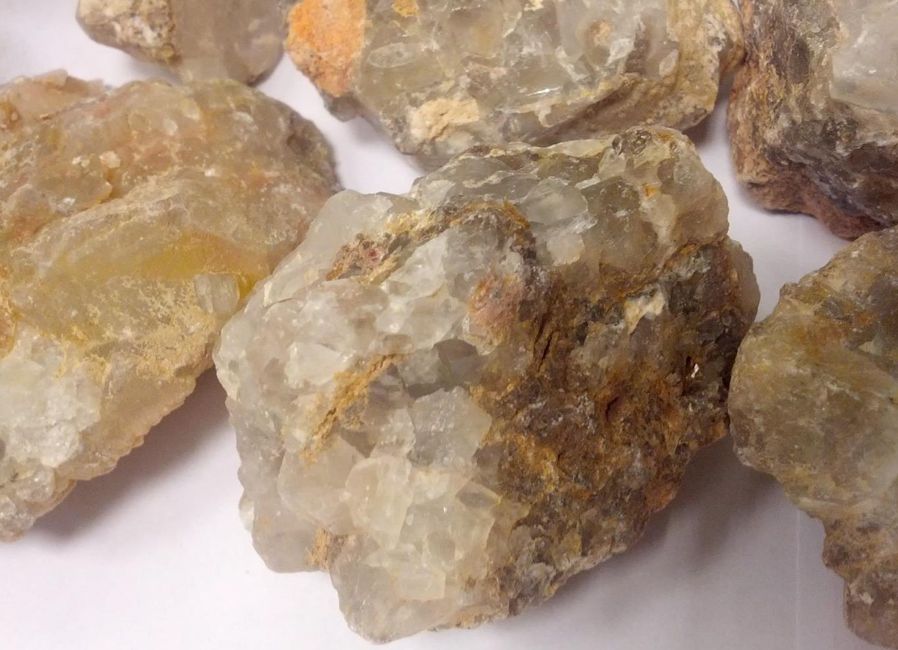
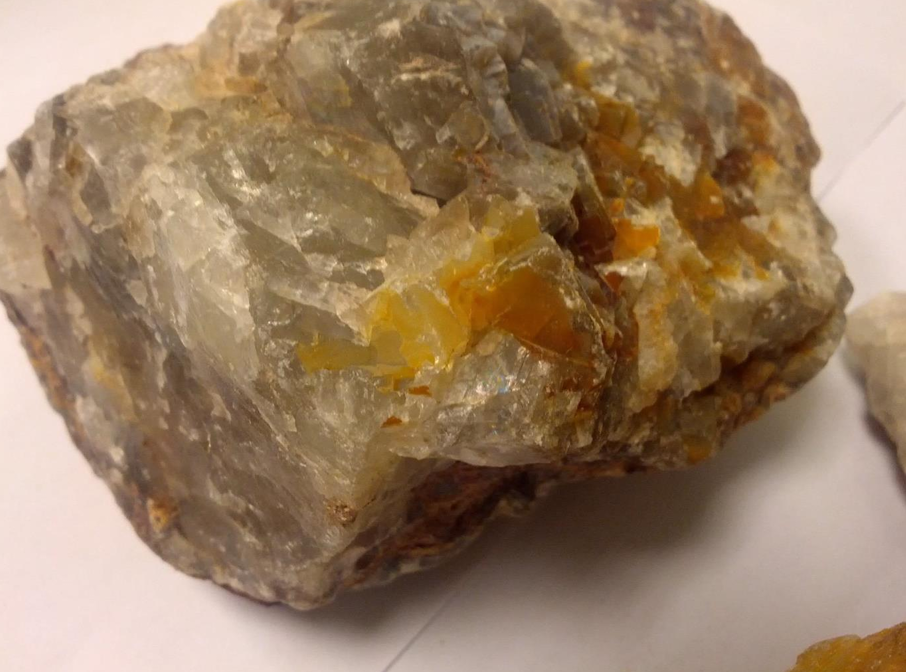
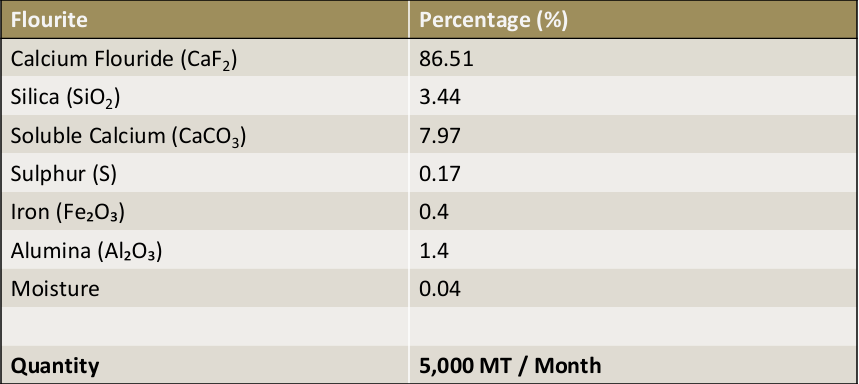
Flourite
Fluorite (also known as fluorspar) has a wide variety of uses. The primary uses are in the metallurgical, ceramics, and chemical industries; however, optical, lapidary, and other uses are also important. Fluorspar, the name used for fluorite when it is sold as a bulk material or in processed form, is sold in three different grades (acid, ceramic, and metallurgical).
Acid Grade Fluorspar
Acid-grade fluorspar is a high-purity material used by the chemical industry. It contains over 97% CaF 2. Most of the fluorspar consumed in the United States is acid grade, even if it is used in lower-grade applications. It is primarily used in the chemical industry to produce hydrofluoric acid (HF). The HF is then used to manufacture a variety of products, including fluorocarbon chemicals, foam blowing agents, refrigerants, and various fluoride chemicals.
Ceramic Grade Fluorspar
Ceramic grade fluorspar contains between 85% and 96% CaF2. Much of this material is used in the manufacture of specialty glass, ceramics, and enamelware. Fluorspar is used to create glazes and surface treatments that produce complex, glossy surfaces, opalescent surfaces, and a variety of other appearances, making consumer glass objects more attractive or more durable. The non-stick cooking surface known as Teflon is made using fluorine derived from fluorite.
Metallurgical Grade Fluorspar
Metallurgical-grade fluorspar contains between 60% and 85% CaF2. A significant portion of this material is utilized in the production of iron, steel, and other metals. Fluorspar can serve as a flux, removing impurities such as sulfur and phosphorus from molten metal and improving the fluidity of the slag. Between 20 and 60 pounds of fluorspar is used for every ton of metal produced. In the United States, many metal producers use fluorspar that exceeds metallurgical grade.
Optical Grade Fluorite
Specimens of fluorite with exceptional optical clarity have been used as lenses. Fluorite has a very low refractive index and a very low dispersion. These two characteristics enable the lens to produce extremely sharp images. Today, instead of using natural fluorite crystals to manufacture these lenses, high-purity fluorite is melted and combined with other materials to produce synthetic "fluorite" lenses of even higher quality. These lenses are used in various optical equipment, including microscopes, telescopes, and cameras.
Lapidary Grade Fluorite
Lapidaries often use specimens of fluorite with exceptional color and clarity to cut gemstones and make ornamental objects. High-quality specimens of fluorite make beautiful faceted stones; however, the mineral is so soft and cleaves so easily that these stones are either sold as collectors' specimens or used in jewelry that will not be subjected to impact or abrasion. Fluorite is also cut and carved into ornamental objects, such as small figurines and vases. These are often treated with a coating or impregnation to enhance their stability and protect them from scratches.
Uses of Fluorite (Fluorspar):
Fluorite, also known commercially as Fluorspar, has a wide range of industrial, chemical, and decorative uses due to its high calcium fluoride (CaF₂) content, optical clarity, and vibrant colors.
> Chemical Industry (Acid Grade Fluorspar): Used to manufacture Hydrofluoric Acid (HF), one of the most important industrial chemicals. HF is then used to produce: Fluorocarbon chemicals,Refrigerants, Foam-blowing agents, Fluoride-based chemicals, Pharmaceuticals, and specialty chemicals.
> Acid Grade fluorspar: is the purest form, containing over 97% CaF₂.2. Ceramic & Glass Industry (Ceramic Grade Fluorspar). Used in the production of specialty glass, ceramics, and enamelware.
> Metallurgical Industry (Metallurgical Grade Fluorspar): Used as a flux in steelmaking and metal processing. Removes impurities like sulfur and phosphorus. Improves slag fluidity, enhancing metal quality. Every ton of steel may require 20–60 lbs of fluorspar.




Specification & Quantity
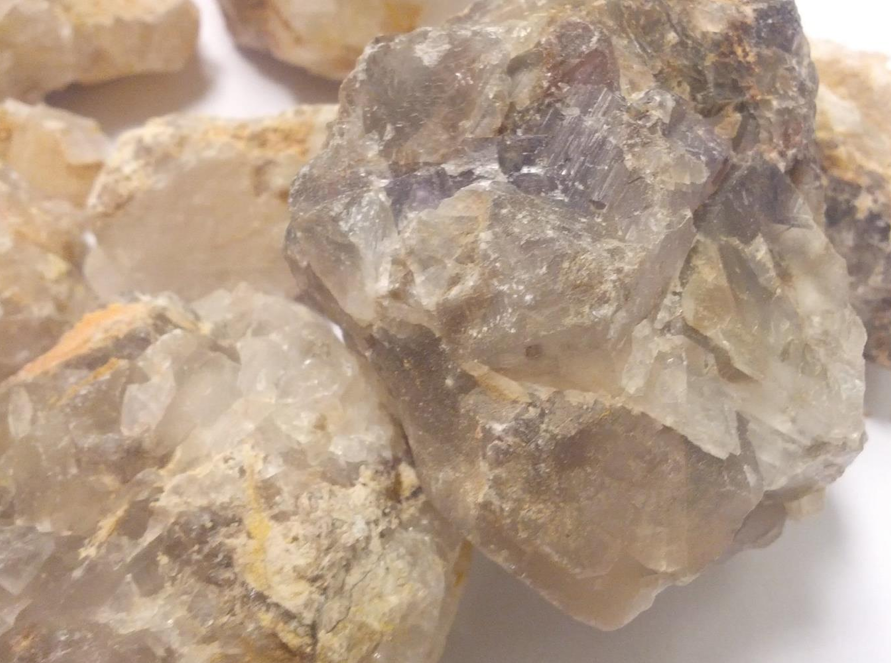
Jade
Jade is a highly valued ornamental mineral known for its beautiful green hues, though it can also occur in white, yellow, and even lavender shades. It has been used for thousands of years in art, jewelry, and cultural artifacts, particularly in East Asia and Central America. Jade is prized for its toughness, smooth texture, and symbolic significance, often representing purity, protection, and prosperity. Its commercial uses extend beyond decorative objects into industrial applications due to its hardness and durability.
Uses of Jade
- Jewelry: rings, necklaces, bracelets, earrings, and pendants
- Carvings: sculptures, figurines, and ornamental objects
- Cultural & Religious Artifacts: amulets, ceremonial tools, and talismans
- Interior Decoration: tiles, inlays, and decorative panels
- Traditional Medicine (in some cultures): massage tools or symbolic wellness items
Industrial & Decorative Uses
Apart from ornamental use, jade has some industrial applications due to its toughness. It can be used in cutting tools, small hand tools, and precise carvings. Historically, jade has been used in architectural elements, ceremonial weapons, and tools due to its exceptional durability. Modern jade continues to be used in interior Decoration, jewelry, and even in small sculptures for meditation or feng shui purposes.
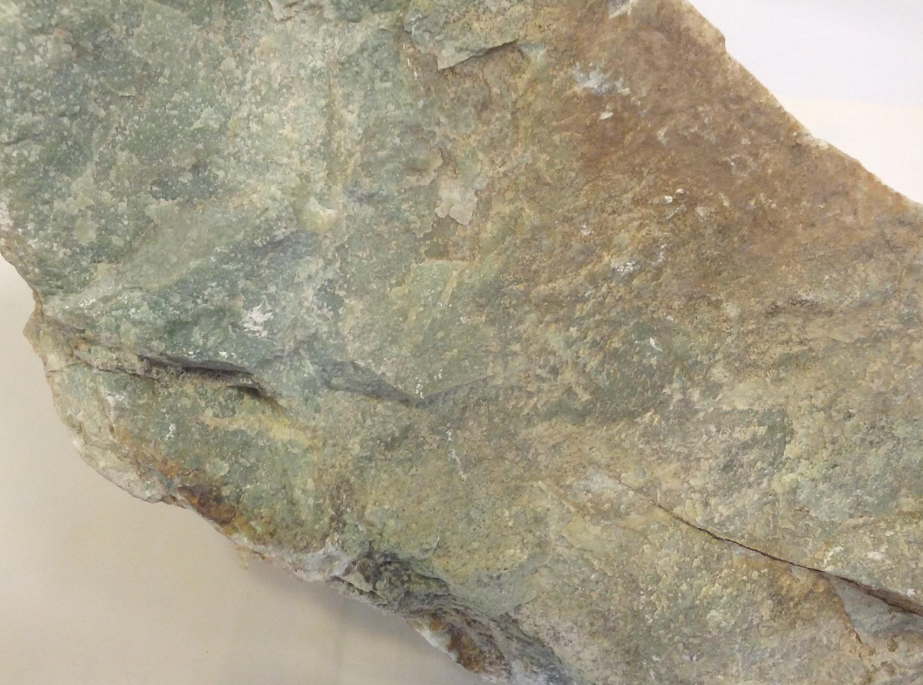
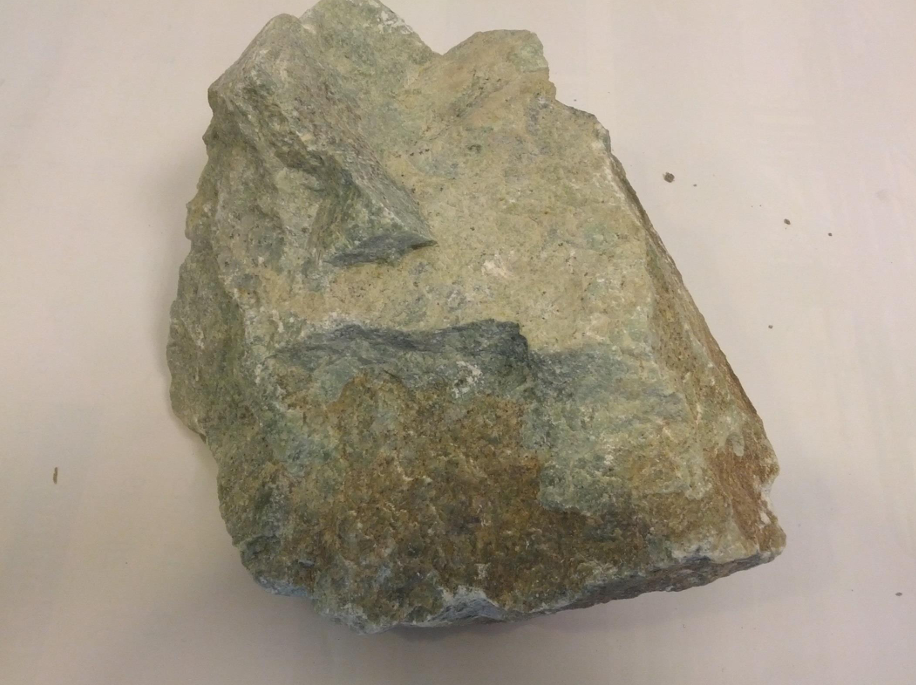
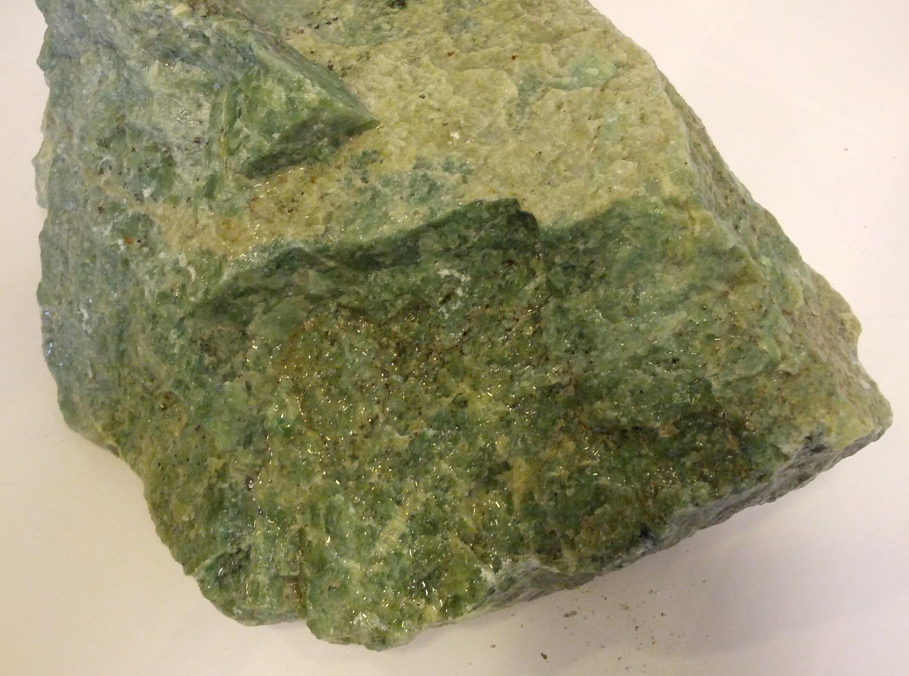
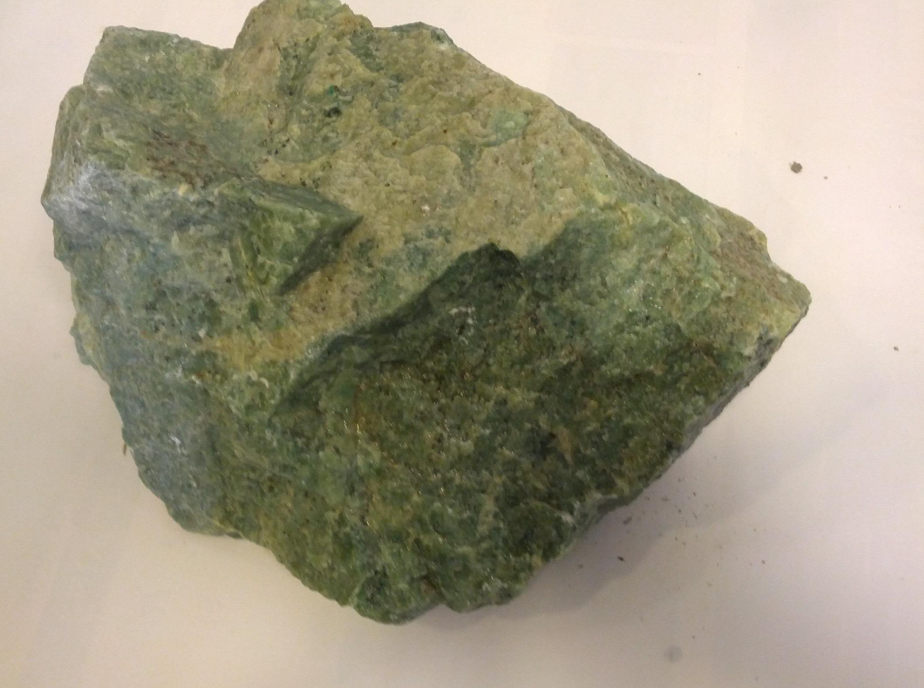











Specification & Quantity
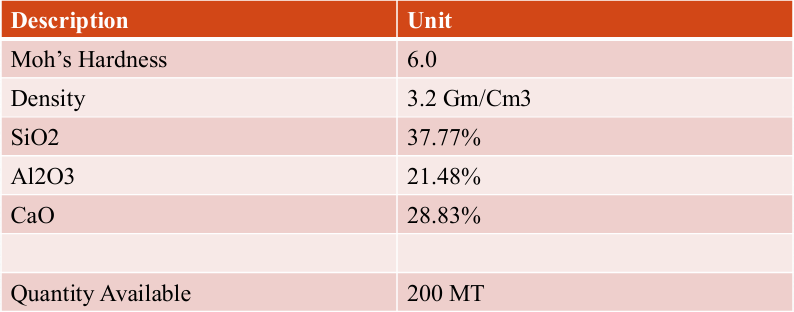
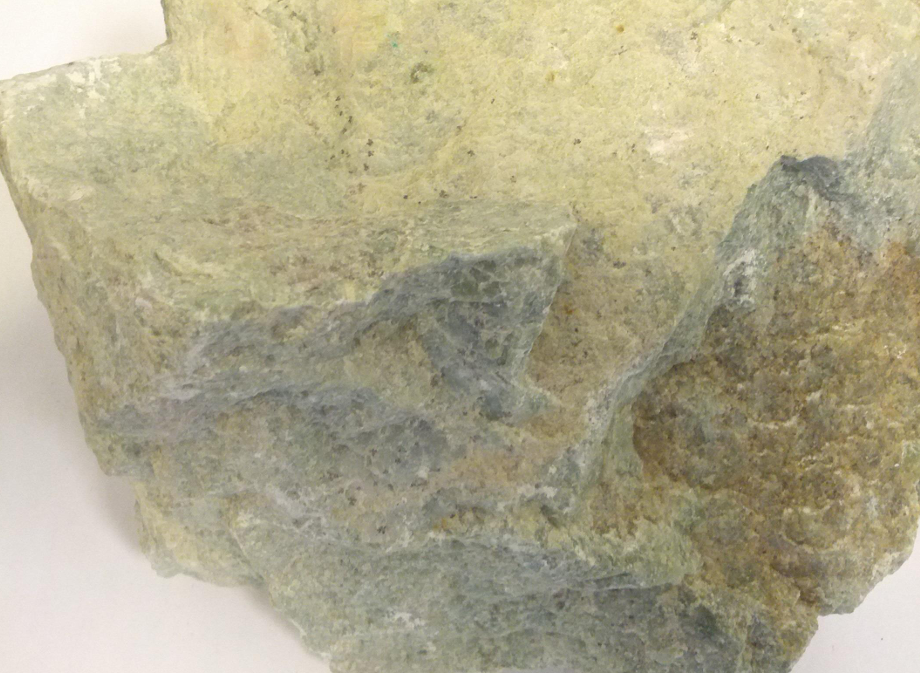
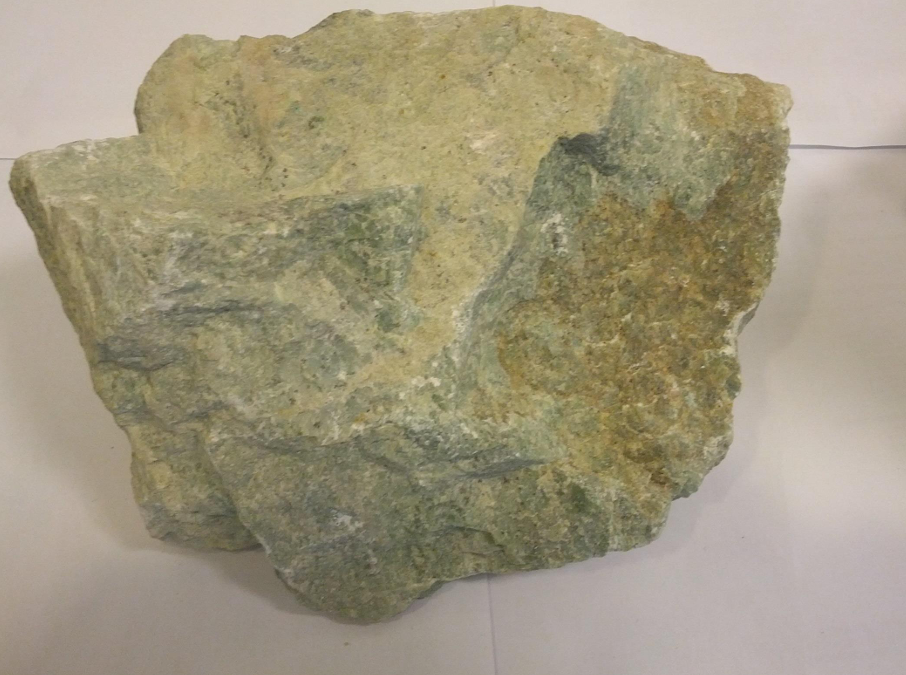
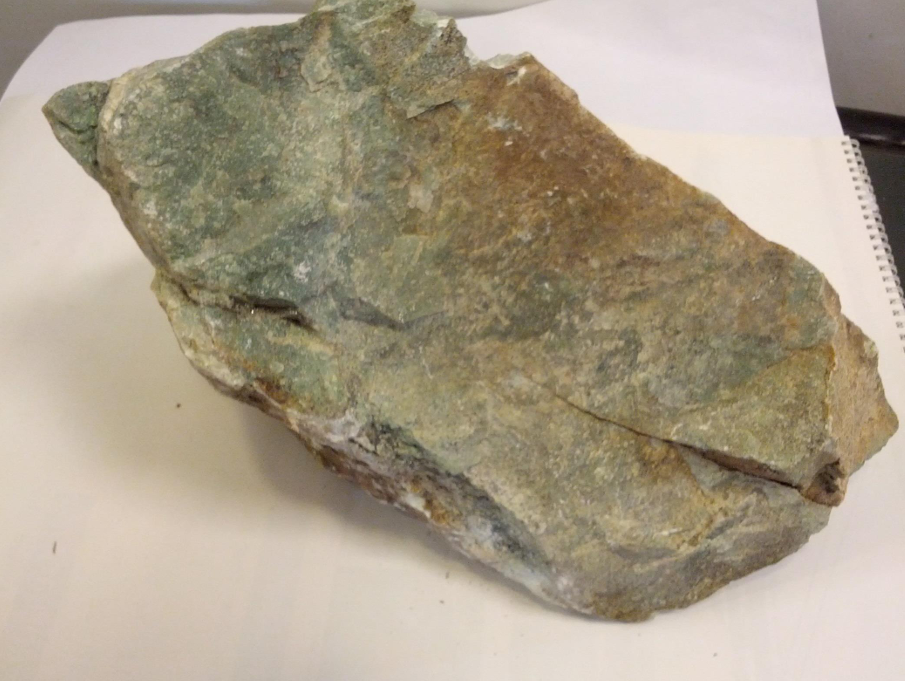
Soapstone (Talc)
Soapstone, also known as talc, is a soft, metamorphic rock primarily composed of talc with varying amounts of chlorite, pyroxenes, micas, amphiboles, carbonates, and other minerals. It is characterized by its smooth, soapy texture and resistance to heat, chemicals, and moisture. Soapstone is available in shades of gray, green, and brown and has been used for centuries in construction, art, and industry due to its durability and workability.
Uses of Soapstone (Talc)
- Industrial Uses:
- Used as a raw material in ceramics, paints, paper, rubber, plastics, and cosmetics.
- Filler in roofing materials and asphalt shingles to improve durability.
- Additive in lubricants, polishing compounds, and insulating materials.
- Decorative Uses:
- Sculptures, ornamental carvings, and countertops due to its smooth texture.
- Fireplaces, stoves, and hearths because of excellent heat resistance.
- Architectural applications such as tiles, wall cladding, and garden ornaments.
- Historical & Cultural Uses:
- Used by ancient civilizations for cookware, ceremonial objects, and jewelry.
Industrial & Decorative Applications:
Soapstone is soft enough to be easily carved yet dense and heat-resistant, making it an ideal material for both functional and ornamental purposes. Industrially, talc-rich soapstone is incorporated into plastics, paints, paper, and rubber to improve texture, durability, and performance. Decoratively, it is favored for countertops, sinks, stoves, and intricate carvings. Its resistance to acids, heat, and moisture allows it to be both aesthetically pleasing and highly functional.
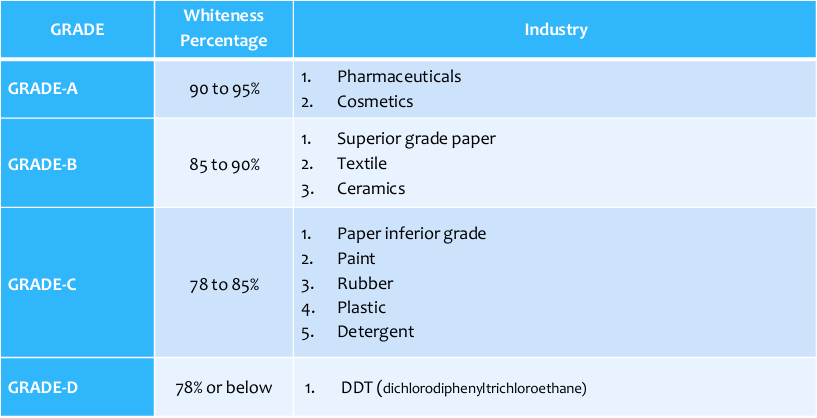
Grade-wise Industrial Use of Soapstone (Talc)
> Grade A — It is known as the first quality material. The color of the mineral is pure white to slightly green. The whiteness is in the range from 90 to 95%. It is used in the production of pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
> Grade B — It is known as the second-grade material. The color is pale-greenish to white. The whiteness is in the range from 85 to 90%. It is used in producing superior-grade paper, textiles, and ceramics.
> Grade C — It is known as the third-grade material. The color is light greenish-grey. Whiteness is in the range from 78 to 85%. It is used in paper (inferior grade), paint, rubber, plastic, and detergent industries.
> Grade D — It is known as the fourth quality or DDT grade. The material with a whiteness of 78% or below is generally classified under this grade. The color of the material is dark greenish-grey to reddish green. The DDT grade material is considered to be of inferior quality.
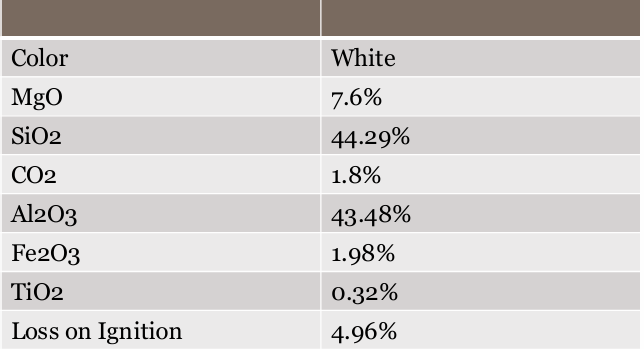
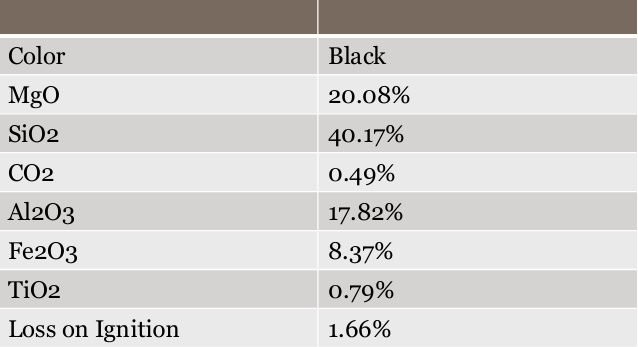
Grade-wise Industrial Usage Table
Soapstone Abbottabad Pure White


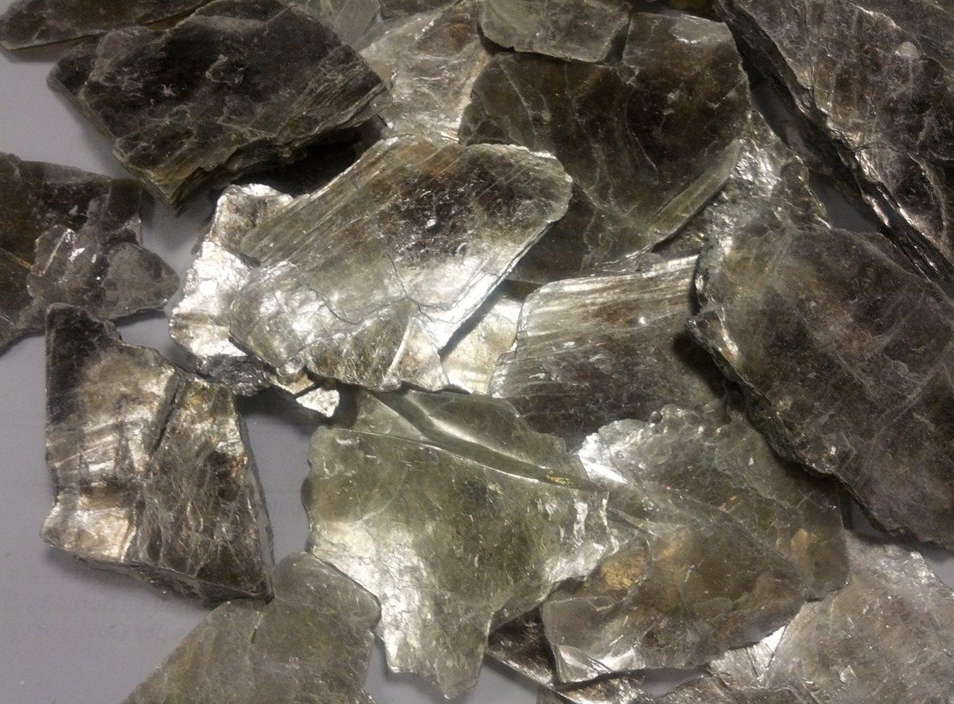
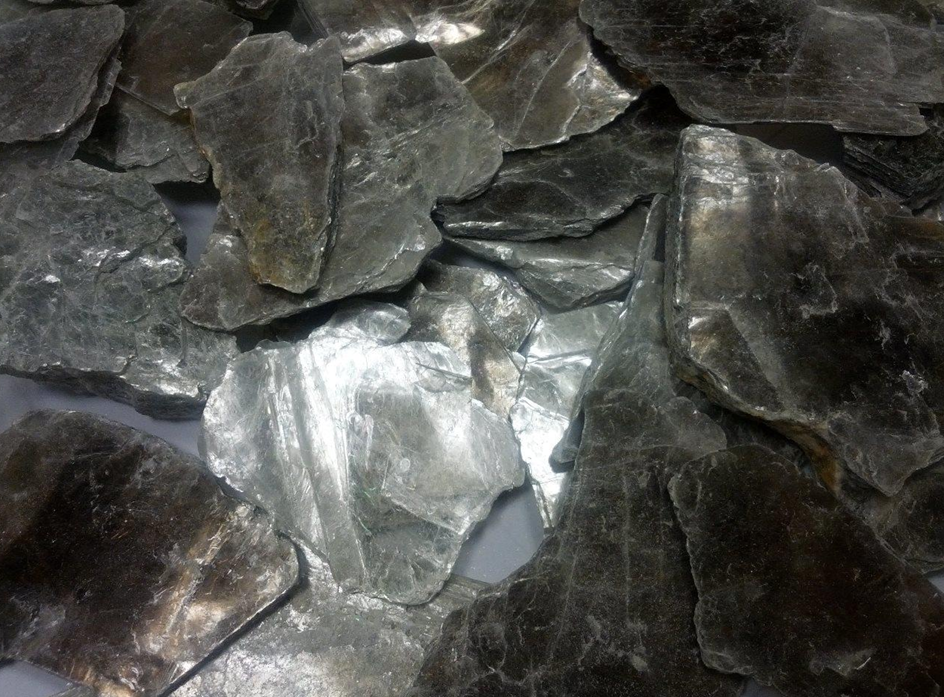
Soapstone Khogyani Dark


Soapstone Khogyani Pure White


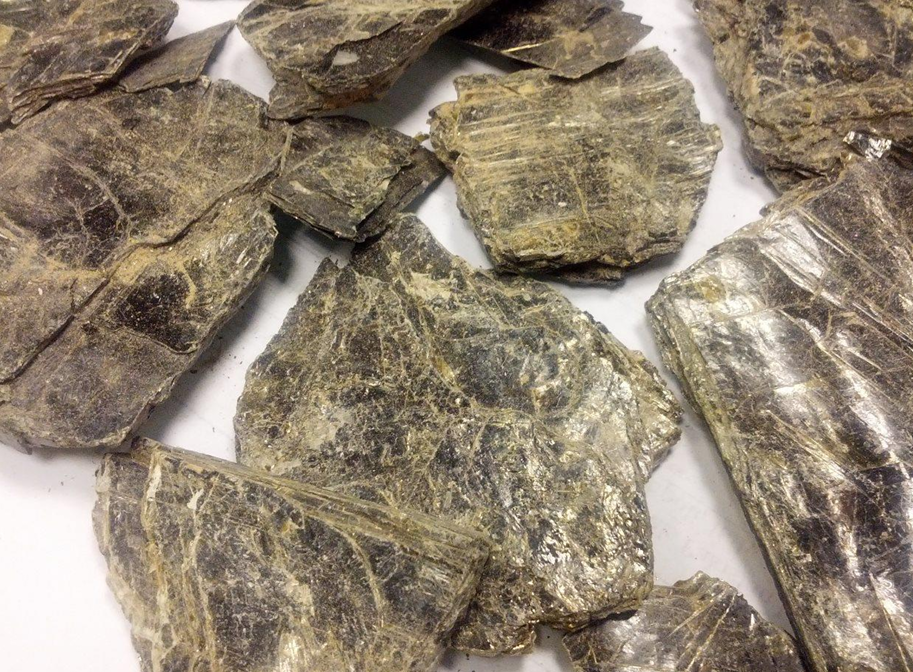
Soapstone Shinwari White


Soapstone Swat Pure White


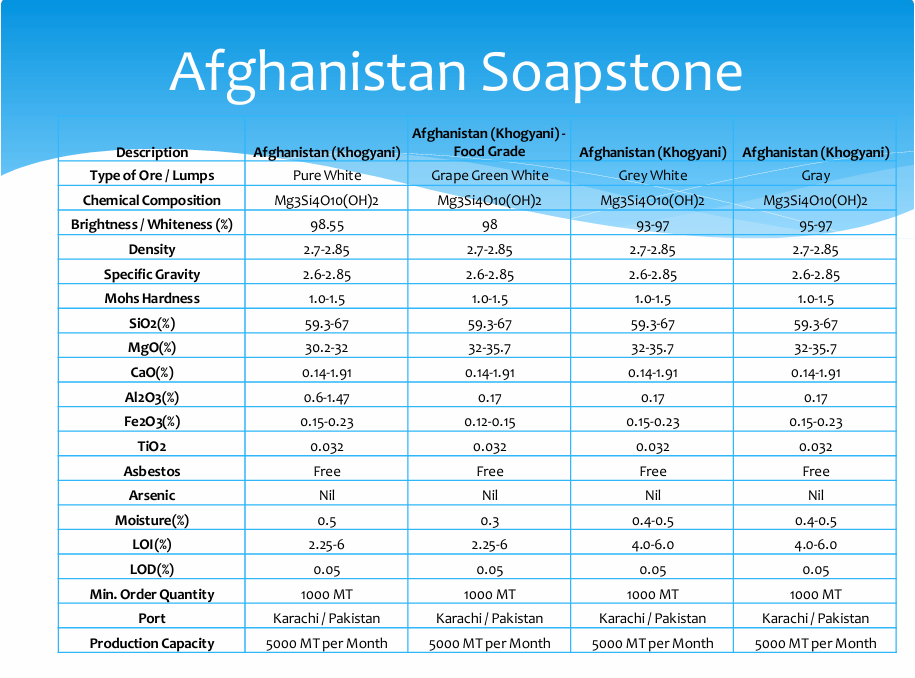
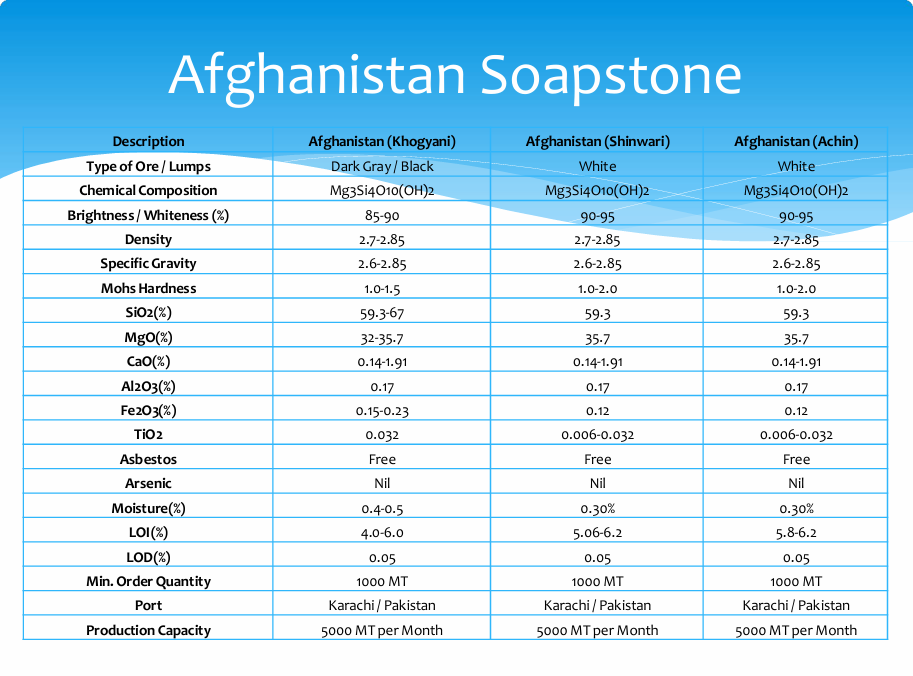
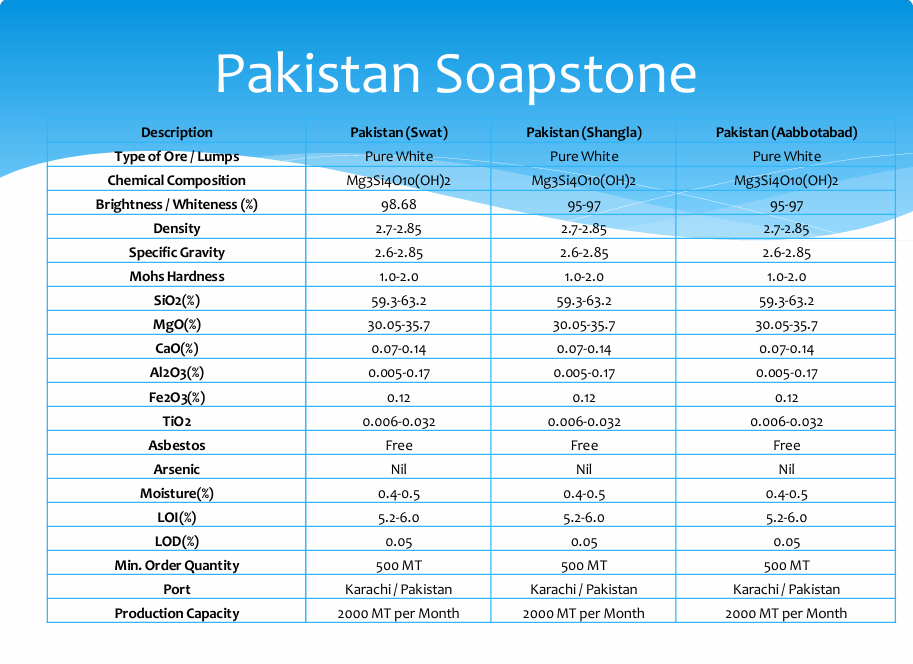
Specifications and Production Capacity
Soapstone Pakistan
Soapstone Afghanistan